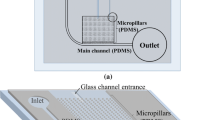
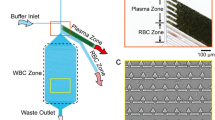
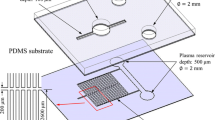
Abstract
We report a comprehensive review on the capillary flow-driven blood plasma separation and on-chip analyte detection in microfluidic devices. Blood plasma separation is the primary sample preparation step prior to most biochemical assays. Conventionally, centrifugation is used for the sample preparation process. There are numerous works reporting blood plasma separation in microfluidic devices which aim at miniaturizing the sample preparation procedure. Capillary-based blood plasma separation shows promise in actualizing point-of-care diagnostic devices for applications in resource-limited settings including military camps and rural areas. In this review, the devices have been categorized based on active and passive plasma separation techniques used for the separation of plasma from capillary-driven blood sample. A comparison between different techniques used for blood plasma separation is outlined. On-chip detection of analytes present in the separated plasma obtained using some of these reported devices is also presented and discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram E (2015) Screening and Diagnostic Tests. Medscape. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/773832-overview. Accessed 20 Nov 2016
AdvaMed (2012) Essentials of Diagnostics. DX Insights, pp 1–14
Aran K, Fok A, Sasso LA, Kamdar N, Guan Y, Sun Q, Undar A, Zahn JD (2011) Microfiltration platform for continuous blood plasma protein extraction from whole blood during cardiac surgery. Lab Chip 11:2858–2868
Bhattacharya S, Datta A, Berg JM, Gangopadhyay S (2005) Studies on surface wettability of poly(dimethyl) siloxane (pdms) and glass under oxygen-plasma treatment and correlation with bond strength. J Microelectromech Syst 14(3):590–597
Bhattacharya S, Gao Y, Korampally V, Othman MT, Grant SA, Kleiboeker SB, Gangopadhyay K, Gangopadhyay S (2007) Optimization of design and fabrication processes for realization of a PDMS-SOG-silicon DNA amplification chip. J Microelectromech Syst 16(2):401–410
Bhattacharya S, Singh RK, Mandal S, Ghosh A, Bok S, Korampally V, Gangopadhyay K, Gangopadhyay S (2010) Plasma modification of polymer surfaces and their utility in building biomedical microdevices. J Adhes Sci Technol 24:2707–2739
Blattert C, Jurischka R, Schoth A, Kerth P, Menz W (2004) Separation of blood cells and plasma in microchannel bend structures. In: Lab-on-a-Chip: platforms, devices, and applications, vol 143, pp 143–151
Chai J, Lu F, Li B, Kwok DY (2004) Wettability interpretation of oxygen plasma modified poly(methyl methacrylate). Langmuir 20:10919–10927
Chen C, Lin P, Chung C (2014) Microfluidic chip for plasma separation from undiluted human whole blood samples using low voltage contactless dielectrophoresis and capillary force. Lab Chip 14:1996
Coulson JM, Richardson JF, Backhurst JR, Harker JH (1991) Chemical engineering volume 2: particle technology and separation processes, 5th edn. Pergamo Press, Oxford
Crowley TA, Pizziconi V (2005) Isolation of plasma from whole blood using planar microfilters for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 5:922–929
Davis JA, Inglis DW, Morton KJ, Lawrence DA, Huang LR, Chou SY, Sturm JC, Austin RH (2006) Deterministic hydrodynamics: taking blood apart. PNAS 103:14779–14784
Dimov IK, Basabe-Desmonts L, Garcia-Cordero JL, Ross BM, Ricco AJ, Lee LP (2011) Stand-alone self-powered integrated microfluidic blood analysis system (SIMBAS). Lab Chip 11:845–850
Faivre M, Abkarian M, Bickraj K, Stone HA (2006) Geometrical focusing of cells in a microfluidic device: an approach to separate blood plasma. Biorheology 43:147–159
Furlani EP (2007) Magnetophoretic separation of blood cells at the microscale. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:1313–1319
Ghubade A, Mandal S, Chaudhury R, Singh RK, Bhattacharya S (2009) Dielectrophoresis assisted concentration of micro-particles and their rapid quantitation based on optical means. Biomed Microdevices 11:987–995
Hosokawa K, Sato K, Ichikawa N, Maeda M (2004) Power-free poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic devices for gold nanoparticle-based DNA analysis. Lab Chip 4(3):181–185
Hou HW, Bhagat AAS, Lee WC, Huang S, Han J, Lim CT (2011) Microfluidic devices for blood fractionation. Micro Mach 2:319–343
Juncker D (2002) Capillary microfluidic systems for bio/chemistry. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Neuchâtel, Anchorage, p 16
Jung JY, Kwak HY (2007) Separation of microparticles and biological cells inside an evaporating droplet using dielectrophoresis. Anal Chem 79(13):5087–5092
Kar S, Maitia TK, Chakraborty S (2015) Capillarity-driven blood plasma separation on paper-based devices. Analyst 140:6473
Kersaudy-Kerhoas M, Sollier E (2013) Micro-scale blood plasma separation: from acoustophoresis to egg-beaters. Lab Chip 13:3323–3346
Khumpuang S, Tanaka T, Aita F, Meng Z, Ooe K, Ikeda M, Omori Y, Miyamura K, Yonezawa H, Matsumoto K, Sugiyama S (2007) Blood plasma separation device using capillary phenomenon. In: 14th International conference on solid-state sensors, actuators and microsystems, france, pp 1967–1970
Kim YC, Kim S, Kim D, Park S, Park J (2010) Plasma extraction in a capillary-driven microfluidic device using surfactant-added poly(dimethylsiloxane). Sens Actuators B Chem 145(2):861–868
Kim Y, Kim K, Park Y (2012) Measurement techniques for red blood cell deformability: recent advances. In: Moschandreou TE (ed) Blood cell—an overview of studies in hematology. InTech, Rijeka, pp 167–194
Kovarik ML, Gach PC, Ornoff DM, Wang Y, Balowski J, Farrag L, Allbritton NL (2012) Micro total analysis systems for cell biology and biochemical assays. Anal Chem 84(2):516–540
Kumar S, Bhushan P, Saha A, Bhattacharya S (2016) Diagnosis of communicable diseases using paper micro-fluidic platforms. In: Cheng C-M, Hsu M-Y, Wu MY-C (eds) Point-of-care diagnostics—new progresses and perspectives. IAPC Open Book and Monograph Platform (OBP), Zagreb
Kuroda C, Ohki Y, Ashiba H, Fujimaki M, Awazu K, Tanaka T, Makishima M (2014) Microfluidic sedimentation system for separation of plasma from whole blood. In: IEEE sensors 2014 proceedings, Valencia, pp 1854–1857
de Laplace PS, Bowditch N (1829) Méchanique céleste, Hillard, Gray, Little and Wilkins, Boston
Lee KK, Ahn CH (2013) A new on-chip whole blood/plasma separator driven by asymmetric capillary forces. Lab Chip 13(16):3261–3267
Li X, Ballerini DR, Shen W (2012) A perspective on paper-based microfluidics: current status and future trends. Biomicrofluidics 6(1):011301–011313
Liana DD, Raguse B, Gooding JJ, Chow E (2012) Recent advances in paper-based sensors. Sensors 12:11505–11526
Madadi H, Casals-Terré J, Mohammadi M (2015) Self-driven filter-based blood plasma separator microfluidic chip for point-of-care testing. Biofabrication 7(2):025007
Manz A, Graber N, Widmer HM (1990) Miniaturized total chemical analysis systems: a novel concept for chemical sensing. Sens Actuators B 1(1–6):244–248. doi:10.1016/0925-4005(90)80209-I
Maria MS, Kumar BS, Chandra TS, Sen AK (2015) Development of a microfluidic device for cell concentration and blood cell-plasma separation. Biomed Microdevices 17:115
Maria MS, Rakesh PE, Chandra TS, Sen AK (2016) Capillary flow based microfluidic device for blood plasma separation and glucose detection. Biomicrofluidics 10:054108
Maria MS, Rakesh PE, Chandra TS, Sen AK (2017) Capillary flow-driven microfluidic device with wettability gradient and sedimentation effects for blood plasma separation. Sci Rep 7:43457. doi:10.1038/srep43457
Mohammadi M, Madadi H, Casals-Terré J, Sellarès J (2015) Hydrodynamic and direct-current insulator-based dielectrophoresis (H-DC-iDEP) microfluidic blood plasma separation. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:4733–4744
Morgan H, Green NG (2003) AC electrokinetics: colloids and nanoparticles. Research Studies Press, Baldock
Mukherjee S, Kang TG, Chen Y, Kim S (2009) Plasma separation from blood: the ‘lab-on-a-chip’ approach. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 37(6):517–529
Nakashima Y, Hata S, Yasuda T (2010) Blood plasma separation and extraction from a minute amount of blood using dielectrophoretic and capillary forces. Sens Actuators B 145:561–569
National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (2012) Types of Blood Tests. US Department of Health and Human Services: National Institutes of Heath. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/bdt/types. Accessed 18 Nov 2016
Noiphung J, Songjaroen T, Dungchai W, Henry CS, Chailapakul O, Laiwattanapaisal W (2013) Electrochemical detection of glucose from whole blood using paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chim Acta 788:39–45
Park S, Shabani R, Schumacher M, Kim Y, Bae Y, Lee K, Cho HJ (2016) On-chip whole blood plasma separator based on microfiltration, sedimentation and wetting contrast. Microsyst Technol 22:2077–2085
Pietrangelo A (2015) Enzyme Markers. Healthline. http://www.healthline.com/health/enzyme-markers#Risks4. Accessed 18 Nov 2016
Sakamoto H, Hatsuda R, Miyamura K, Sugiyama S (2012) Plasma separation PMMA device driven by capillary force controlling surface wettability. Micro Nano Lett 7(1):64–67
Son JH, Lee SH, Hong S, Park S, Lee J, Dickey AM, Lee LP (2014) Hemolysis-free blood plasma separation Hemolysis-free blood plasma separation. Lab Chip 14:2287
Songjaroen T, Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS, Laiwattanapaisal W (2012) Blood separation on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Lab Chip 12:3392–3398
Swiss Precision Diagnostics GmbH (1985) Clearblue Pregnancy Tests. Clearblue. http://uk.clearblue.com/. Accessed 10 Nov 2016
Szydzik C, Khoshmanesh K, Mitchell A, Karnutsch C (2015) Microfluidic platform for separation and extraction of plasma from whole blood using dielectrophoresis. Biomicrofluidics 9:064120
Toner M, Irimia D (2005) Blood-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7:77–103
Tripathi S, Kumar YVBV, Prabhakar A, Joshi SS, Agrawal A (2015) Passive blood plasma separation at the microscale: a review of design principles and microdevices. J Micromech Microeng 25(8):083001
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373. doi:10.1038/nature05058
Wu C, Hong L, Ou C (2012) Blood cell-free plasma separated blood samples with a cascading weir-type microfilter using dead-end Filtration. J Med Biol Eng 32(3):163–168
Yang X, Forouzan O, Brown TP, Shevkoplyas SS (2012) Integrated separation of blood plasma from whole blood for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Lab Chip 12:274
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge SERB, DST, India (EMR/2014/001151), and IIT Madras (MEE1516843RFTPASHS) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maria, M.S., Chandra, T.S. & Sen, A.K. Capillary flow-driven blood plasma separation and on-chip analyte detection in microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 21, 72 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1907-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1907-6